

They do this by functioning at times as the past tense forms of their fellow modal verbs can, may, shall, and will. Only a few of the core modal verbs have the ability to refer to past time: could, might, should, and would. Using a modal verb in the simple past or the present perfect (which indicates an action that happened in the past but is directly related to the present) is a little trickier. We already covered the simple present above, but you can also use modal verbs in the present continuous and present perfect continuous tenses.Īfter the modal verb, use the word be followed by the – ing form of the main verb: + be +. However, all of them can be used with different conjugations of a sentence’s main verb to refer to present or future time in different ways, so let’s talk a little about verb tenses and modal verbs.
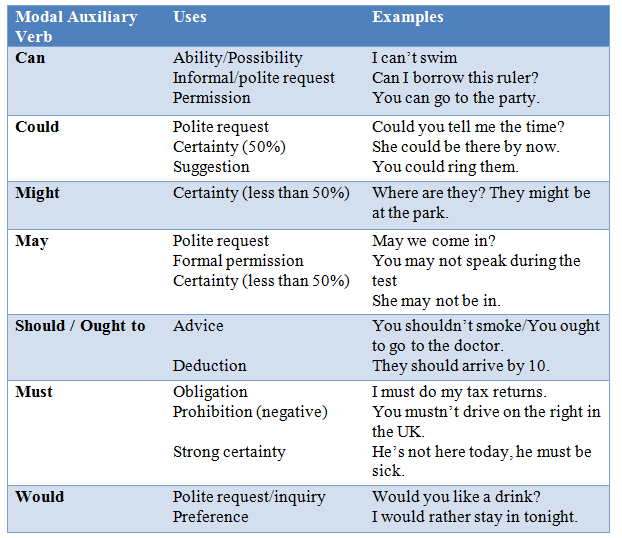
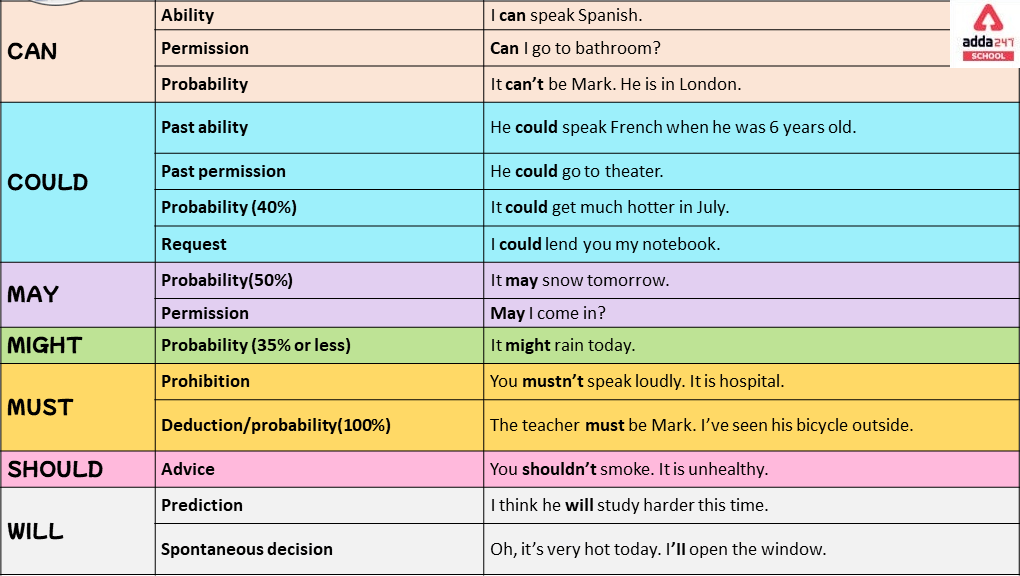
Note that in the second example above, because have is a verb that only sometimes functions as an auxiliary verb and at other times functions as a main verb, the question is formed with the auxiliary verb do at the beginning.īecause modal verbs deal largely with general situations or hypotheticals that haven’t actually happened, all of the core ones can refer to present and future time but only some of them can refer to past time, and most of the time they do not change form to make different tenses. In these cases, you can use the modal verbs should and must to show probability without certainty. Some things seem likely to be true but can’t be stated as definite facts. What special conditions do modal verbs indicate? Here’s a list, along with examples: Likelihood Some modal verbs express very specific conditions that don’t come up often, like dare in its modal form in “Dare I ask?” The word used in the idiomatic phrase used to, as in “I used to be an English student too,” behaves like a modal verb with only a past tense form. There are also verbs that can function either as main verbs or as modal auxiliaries depending on the context got, need, and have all behave like modal verbs in the common colloquial expressions got to, need to, and have to. Some-like shall and ought-are rarely used any longer. There are other, less common modal verbs. Modal verbs are quite common in English you’ve seen them in action hundreds of times even if you didn’t know what they were called.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
